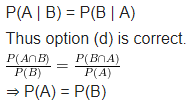NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Probability
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Probability is designed and prepared by the best teachers across India. All the important topics are covered in the exercises and each answer comes with a detailed explanation to help students understand concepts better. These NCERT solutions play a crucial role in your preparation for all exams conducted by the CBSE, including the JEE.
Chapter 13 Probability Solutions covers multiple exercises. The answer to each question in every exercise is provided along with complete, step-wise solutions for your better understanding. This will prove to be most helpful to you in your home assignments as well as practice sessions.
The topics and sub-topics included in Chapter 13 Probability the following:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 13 | Probability |
| 13.1 | Introduction |
| 13.2 | Conditional Probability |
| 13.3 | Multiplication Theorem on Probability |
| 13.4 | Independent Events |
| 13.5 | Bayes’ Theorem |
| 13.6 | Random Variables and its Probability Distributions |
| 13.7 | Bernoulli Trials and Binomial Distribution |
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Probability Ex 13.1
Question 1
Given that E and Fare events such that
P (E) = 0.6, P (F) = 0.3 and P(E∩F) = 0.2
find P(E|F) and P (F|E).
Solution:
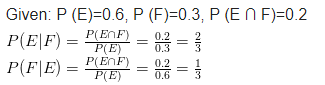
Question 2
Compute P(A|B) if P(B)=0.5 and P (A∩B) = 0.32.
Solution:
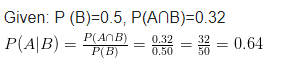
Question 3.
If P (A)=0.8, P (B)=0.5 and P(B/A)=0.4, find
(i) P(A∩B)
(ii) P(A/B)
(iii)P(A∪B)
Solution:
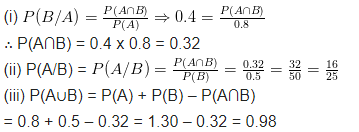
Question 4.
Evaluate P(A∪B) if 2P(A) = P(B) = and P(A|B) =
.
Solution:
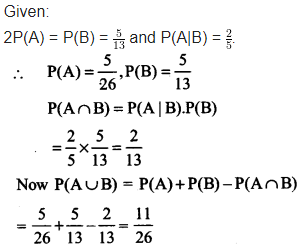
Question 5.
If P(A) = ,P(B) =
and P(A∪B) =
,
Find
(i) P(A∩B)
(ii) P(A|B)
(iii) P(B|A)
Solution:
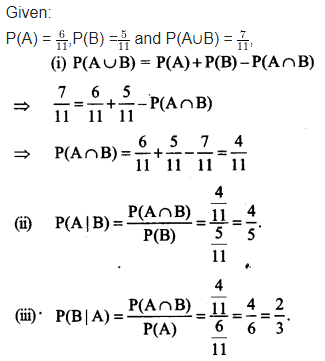
Question 6.
Determine P(E/F) in question 6 to 9:
A coin is tossed three times, where
(i) E: head on third toss F: heads on first two tosses.
(ii) E: at least two heads F : at most two heads
(iii) E: at most two tails F: at least one tail
Solution:

Question 7.
Two coins are tossed once
(i) E: tail appears on one coin F: one coin shows head
(ii) E: no tail appears F: no head appears.
Solution:
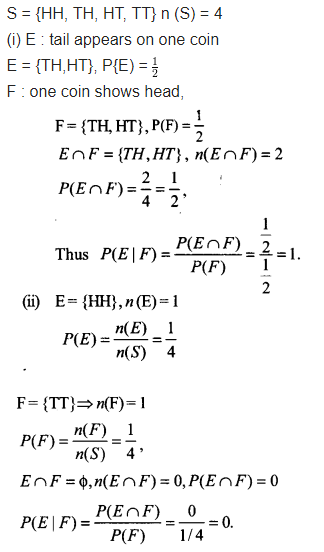
Question 8.
A die is thrown three times.
E: 4 appears on the third toss
F: 6 and 5 appears respectively on first two tosses.
Solution:

Question 9.
Mother, father and son line up at random for a family picture:
E: son on one end, F: father in middle
Solution:

Question 10.
A Mack and a red die are rolled.
(a) Find the conditional probability of obtaining a sum greater than 9, given that the black die resulted in a 5.
(b) Find the conditional probability of obtaining the sum 8, given that the red die resulted in a number less than 4.
Solution:

Question 11
A fair die is rolled. Consider events E = {1,3,5} F = {2,3} and G = {2,3,4,5}, Find
(i) P(E|F) and P(F|E)
(ii) P(E|G) and P(G|E)
(iii) P((E ∪ F) |G) and P (E ∩ F)|G)
Solution:
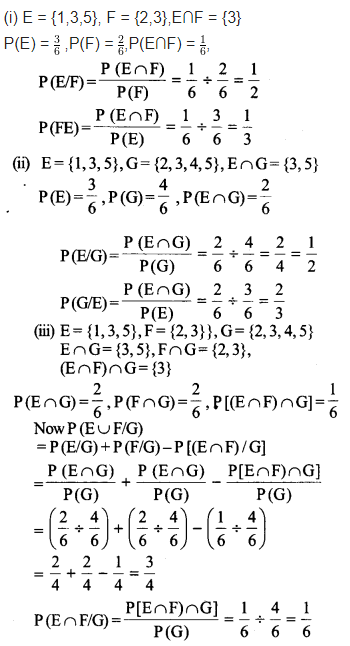
Question 12.
Assume that each child born is equally likely to be a boy or a girl. If a family has two children, what is the conditional probability that both are girls given that
(i) the youngest is a girl,
(ii) at least one is girl?
Solution:

Question 13.
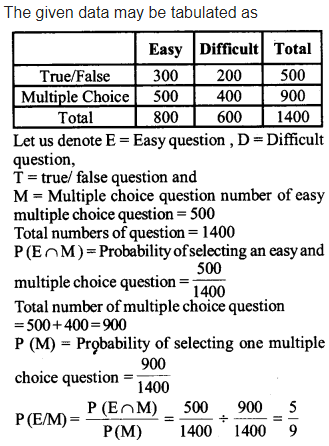
An instructor has a question bank consisting of300 easy True/ False questions, 200 difficult True/ False questions, 500 easy multiple choice questions and 400 difficult multiple choice questions. If a question is selected at random from the question bank, what is the probability that it will be an easy question given that it is a multiple choice question?
Solution:
Question 14.
Given that the two numbers appearing on throwing two dice are different. Find the probability of the event ‘the sum of numbers on the dice is 4’.
Solution:

Question 15.
Consider the experiment of throwing a die, if a multiple of 3 comes up, throw the die again and if any other number comes, toss a coin. Find the conditional probability of the event ‘the coin shows a tail’ given that ‘at least one die shows a 3’.
Solution:


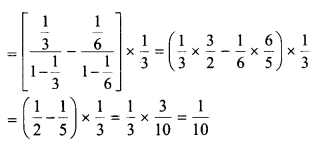
In each of the following choose the correct answer:
Question 16.
If P(A) = , P (B) = 0 then P (A | B) is
(a) 0
(b)
(c) not defined
(d) 1
Solution:
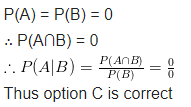
Question 17.
If A and B are events such that P(A | B) = P(B | A) then
(a) A⊂B but A≠B
(b) A = B
(c) A∩B = φ
(d) P(A) = P(B)
Solution: