Bank Reconciliation Statement Class 11 Notes Accountancy Chapter 5
We know that Banks provide very important financial services in modern society. These days a large number of cash transactions are in fact passed through banks. Usually, all the business firms open a current account with a bank, and in order to record the transactions entered into with the bank, maintain a Bank Column in the Cash Book. Bank also maintains an account for each customer in its books.
All deposits by the customer are recorded on the credit side of his/her account and all withdrawals are recorded on the debit side of his/her account. A copy of this account is regularly sent to the customer by the bank. This is called ‘Pass Book’ or ‘Bank Statement’. The amount of balance shown in the passbook or the bank statement must tally with the balance as shown in the cash book. The businessman has to ascertain the cause for such a difference.
Meaning of Bank Reconciliation Statement:
According to Patil, “Bank reconciliation statement is a statement prepared mainly to reconcile the difference between the ‘Bank Balance’ shown by the Cash Book and Bank Pass Book.”
In other words, Bank Reconciliation Statement is a statement of account that explains the reasons for any difference between the bank balance as per cash book and bank balance as per bank statement/passbook and reconciles the two.
In simple words, it is generally experienced that where a comparison is made between the bank balance as shown in the firm’s cash book and the bank balance as shown in the bank passbook, the two balances do not tally/Hence, we have to first ascertain the causes of difference thereof and then reflect them in a statement called Bank Reconciliation Statement to reconcile (tally) the two balances.
Need for Reconciliation:
It is neither compulsory to prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement nor the date is fixed on which it is to be prepared. It is prepared from time to time to check that all transactions relating to the bank are properly recorded by the businessman in the bank column of the cash book and by the bank in its ledger account. Thus, it is prepared to reconcile the bank balances shown by the cash book and by the bank statement. It helps in detecting if there is an error in recording the transactions and ascertaining the correct bank balances as a particular date.
Reasons or Causes of Difference in the balance of the Cash Book and Pass Book
Reconciliation of the cash book and the bank passbook balances amounts to an explanation of differences between them. The differences between the cash book and the bank passbook is caused by:
- Timing differences on a recording of the transactions
- Errors made by the business or by the bank.
1. Timing Difference:
(a) Cheques issued by the firm but not yet presented for payment in the bank.
(b) Cheques paid or deposited into the bank but not yet collected.
(c) Bank charges or other charged, charges by the bank on behalf of the customer.
(d) Amount collected or credited by bank on standing instructions given by the customers.
(e) Amount paid or debited by the bank on standing instructions given by the customer.
(f) Interest credited by the bank.
(g) Interest debited by bank or overdraft.
(h) Direct payment by the customer into the bank account.
(i) Dishonour of cheques or bills.
2. Differences caused by errors
(a) Errors committed in recording transactions by the firm.
(b) Errors committed in recording transactions by the bank.
Preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement
After identifying the causes of difference, the reconciliation may be done in the following two ways:
(a) Preparation of bank reconciliation statement without adjusting cash book balances.
(b) Preparation of bank reconciliation statement after adjusting cash book balance.
Preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement without adjusting cash book balances
We may have two types of balances while preparing the Bank Reconciliation Statement which is following:
(a) Favourable balances
- Credit balance as per passbook or bank statement is given and the balance as per cash book is to be ascertained.
- Debit balance as per cash book is given and the balance as per pass book is to be ascertained.
(b) Unfavourable balances
- Debit balance as per pass book (i.e. overdraft) is given and the balance as per cash book is to be ascertained.
- Credit balance as per cash book (i.e. overdraft) is given and the balance as per pass book is to be ascertained.
Steps are to be taken for preparation of the Bank Reconciliation Statement
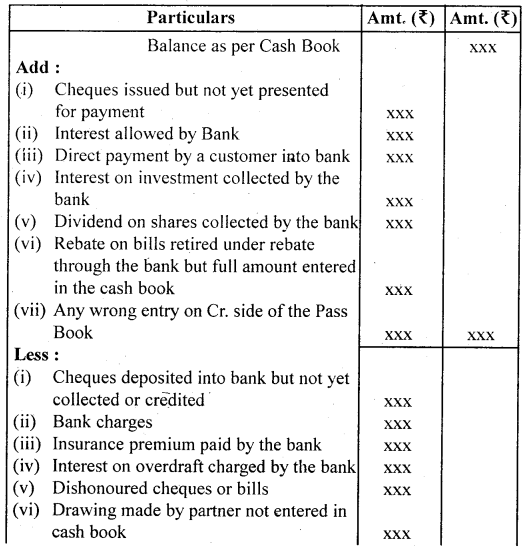
1. When debit balance as per Cash Book (Favourable balance) is given:
- Take balance as a starting point say Balance as per Cash Book.
- Add all transactions that have resulted in increasing the balance of the passbook.
- Deduct all transactions that have resulted in decreasing the balance of the passbook.
- Extract the net balance shown by the statement which should be the same as shown in the passbook.
Proforma:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as on…………..

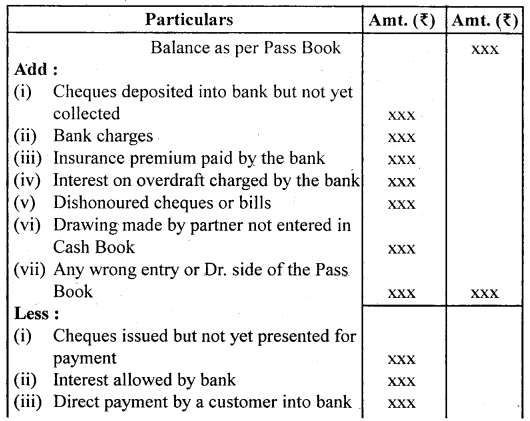
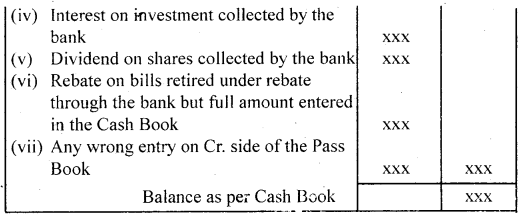
2. When the credit balance as per Pass Book (Favourable balance) is given:
- Take balance as a starting point say Balance as per Pass Book.
- Add all transactions that have resulted in increasing the balance of the cash book.
- Deduct all transactions that have resulted in decreasing the balance of the cash book.
- Extract the net balance shown by the statement which should be the same as shown in the cash book.
Proforma:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as on…………..
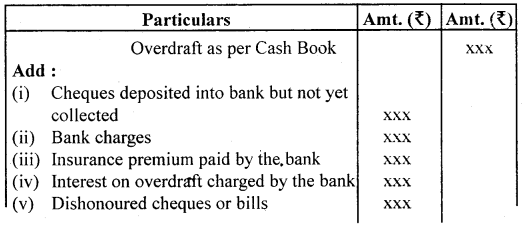
3. When the credit balance as per Cash Book (Uufavoarable balance) is given:
- Take balance as a starting point say Overdraft as per Cash Book.
- Add all the transactions that have resulted in decreasing the balance of the passbook.
- Deduct all the transactions that have resulted in increasing the balance of the passbook.
- Extract the net balance shown by the statement which should be the same as shown in the passbook.
Proforma:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as on……………..
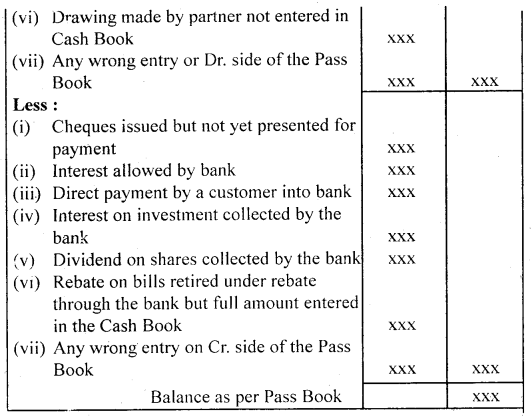
4. When the debit balance as per Pass Book (Unfavourable balance) is given:
- Take balance as a starting point say overdraft as per Pass Book.
- Add all the transactions that have resulted in decreasing the balance of the cash book.
- Deduct all the transactions that have resulted in increasing the balance of the cash book.
- Extract the net balance shown by the statement which should be the same as shown in the cash book.
Proforma:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as on…………….
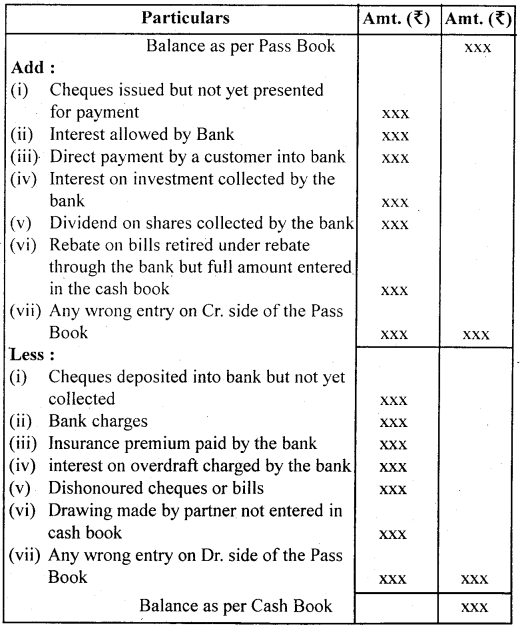
Preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement with Adjusted Cash Book
Bank Reconciliation Statement is prepared usually without adjusting the Cash Book during the different months of the financial year. However, at the. end of the financial year, the Cash Book must be adjusted before preparing the Bank Reconciliation Statement as the adjusted balance of the Cash Book is to be shown in the Balance Sheet.
The procedure for finding out adjusted cash balance is as follows:
1. Firstly a Cash Book with Bank Columns only will be prepared with the balance of the existing Cash Book.
2. All errors that have been committed in the Cash Book will have to be rectified by passing adjusting entries in the Cash Book.
For example:
(a) Any amount recorded twice in the Cash Book.
(b) Recording of issued cheques omitted in Cash Book.
(c-) Cheques deposited into the bank but omitted to be recorded in • Cash Book.
(d) Overcosting or undercoating of debit or credit column of Cash Book.
(e) Entries on the wrong side of columns etc.
3. Amounts for which bank has given credit in Pass Book but not recorded in the debit side of Cash Book. They will be recorded.
(a) Interest allowed by the bank.
(b) Interest Or dividend collected by the bank.
(c) Amount directly deposited by customers into bank etc.
4. Amounts for which bank has given debit in Pass Book but not recorded in the credit side of Cash Book. They will be recorded, such as
(a) Interest charged by the bank on overdraft.
(b) Bank charges, commission charges, etc.
(c) Insurance premium paid by the bank.
(d) cheque sent for collection and dishonored.
5. Following items must not be recorded in the Amended/Adjusted Cash Book:
(a) Cheques deposited into the bank but not collected.
(b) Cheques issued but not presented for payment.
(c) Any wrong entry in Pass Book.
6. Adjusted Cash Book is then balanced and this new balance is taken as a starting point for preparing the Bank Reconciliation Statement.