CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Notes Sources of Energy
Sources of Energy Class 10 Notes Understanding the Lesson
Characteristics of a good fuel
- High calorific value (gives more heat per unit mass).
- Bums without giving out any smoke or harmful gases.
- Proper ignition temperature.
- Cheap and easily available.
- Easy to handle, safe to transport.
- Convenient to store.
- Burns smoothly.
Classification of sources of energy
1. On the basis of use
- Conventional sources of energy.
- Non-conventional sources of energy
- Conventional sources of energy are those which are used extensively and meet a major portion of our energy requirement.
Examples:
(a) Fossil fuels,(b) Thermal power plant,(c) Hydropower plant,(d) Biomass,(e) Wind energy. - Non-conventional sources of energy are those which are not used as the conventional ones and meet our energy requirements only on a limited scale.
Examples:
(a) Solar energy,(b) Nuclear energy,(c) Tidal and wave energy,(d) Geothermal energy
2. On the basis of quantity available
- Renewable sources of energy
- Non-renewable sources of energy
- Renewable sources of energy are those which are inexhaustible i.e., which can be replaced as we use them and can be used to produce energy again and again.
Examples:
(a) Solar energy,(b) Wind energy - Non-renewable sources of energy are those which are exhaustible and cannot be replaced once they have been used.
Examples: (a) Fossil fuel
Conventional sources of energy
1. Fossil fuels: Fossil fuels were formed millions of year ago, when plant and animal remains got buried under the Earth and were subjected to high temperature and pressure conditions.
Examples: Coal and petroleum
These are non-renewable sources of energy:
Pollution Caused by Fossil Fuels
- Released oxides of carbon, nitrogen and sulphur (acidic in nature) which causes acid rain that damages trees, plants, reduces fertility of soil.
- Produces large amount of CO2 in the atmosphere which causes greenhouse effect leading to excessive heating of the Earth.
Controlling Pollution Caused by Fossil Fuels
- Increasing the efficiency of the combustion process.
- Using various techniques to reduce the escape of harmful gases and ashes into the surroundings.
2. Thermal Power Plant
A power plant which uses heat energy to generate electricity.
- Burning of fossil fuels produces steam to run turbines.
- Set up (power plants) near the coal and oil fields to minimise the cost of transportation and production.
- Transmission of electricity is more efficient.
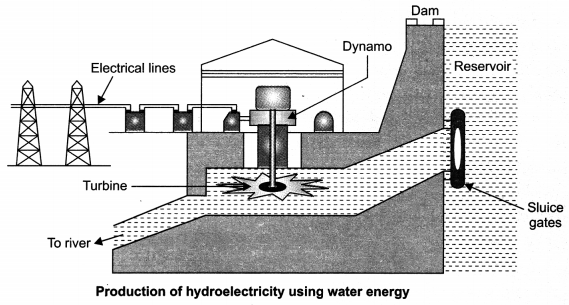
3. Hydro Power Plants
- Dams are constructed to collect water flowing in high altitude rivers. The stored water has a lot of potential energy.
- When water is allowed to fall from a height, potential energy changes to kinetic energy, which
- rotates the turbines to produce electricity.
Advantages
- No environmental pollution
- Flowing water is a renewable source of electric energy.
- Construction of dams prevents flooding of rivers, provide water for irrigation.
Disadvantages
- Large areas of agricultural land, a vast variety of flora and fauna, human settlements get submerged in the water of reservoir formed by the dam.
- Large ecosystems are destroyed.
- Vegetation that submerged under water rots under anaerobic conditions and produces large amount of methane which is a greenhouse gas.
- Creates problems of satisfactory rehabilitation of displaced people.
- Dams are highly expensive to construct.
- Dams cannot be constructed on all river sites.
4. Biomass
The dead parts of plants and trees and the waste materials of animals are called Biomass.
(i) Wood: It is a biomass and used as a fuel for a long time.
Disadvantages
- Produces a lot of smoke on burning.
- Do not produce much heat.
- Thus by improvement in technology we can improve the efficiency of traditional sources of energy.
For example, wood can be converted into much better fuel called charcoal.
(ii) Charcoal: When wood is burnt in a limited supply of air, then water and other volatile materials gets removed and charcoal is formed.
![]()
Charcoal is a better fuel than wood because
- it has a higher calorific value than wood.
- it does not produce smoke while burning.
- it is a compact fuel, easy to handle and convenient to use.
(iii) Cow dung: It is biomass but it is not good to burn cowdung directly as fuel because it
- produces a lot of smoke.
- does not burn completely, produces a lot of ash as residue.
- has low calorific value.
by making biogas (or gobar gas) from cow dung, we get a smokeless fuel.
(iv) Biogas: It is mixture of gases produced during decomposition of biomass in the absence of oxygen.
- Methane is major component of biogas. Biogas contains 75% methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide.
- Biogas is produced in a biogas plant using animal dung, sewage, crop residues, vegetable wastes, poultry dropping, etc.
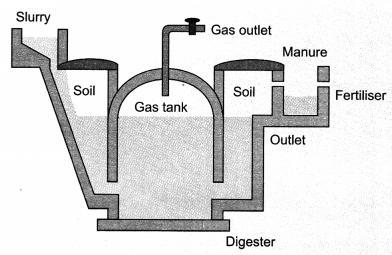
Biogas plant: Construction and Working
The plant has dome like structure built with bricks. A slurry of cow dung and water is made in the mixing tank from where it is fed into the digester. The digester is a sealed chamber in which there is no oxygen. Anaerobic microorganisms that do not require oxygen, decompose or breakdown complex compound of cow slurry and produces methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide.
Advantages of Biogas
- It is an excellent fuel as it contains upto 75% methane (CH4).
- It burns without smoke.
- Leaves no residue like ash in wood and coal burning.
- Heating capacity is high.
- It is also used for lighting.
- Slurry left behind is used as excellent manure rich in nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Safe and efficient method of waste disposal.
5. Wind energy
- Unequal heating of the landmass and water bodies by solar radiations generate air movement and causes wind to blow.
- Kinetic energy of the wind can be used:
o to generate electricity by turning the rotor of the turbine, o to lift water from the well, o to run flour mills. - But the output of a single windmill is quite small so a number of windmills are erected over a large area called wind energy farm.
- The minimum wind speed for windmill to serve as a source of energy is 15-20 km/per hour.
Advantages
- Eco-friendly
- Efficient source of renewable energy
- No recurring expenses for production of electricity.
Disadvantages
- Wind energy farms need large area of land.
- Difficulty in getting regular wind speed of 15-20 km/per hour.
- Initial cost of establishing wind energy farm is very high.
- High level of maintenance of blades of windmill.
Alternate or Non-conventional Sources of Energy
Day by day, our demand for energy is increasing, so there is a need for another source of energy.
Reasons for alternate sources of energy
- The fossil fuel reserves in the Earth are limited which may get exhausted soon if we use them at the current rate.
- Reduce the pressure on fossil fuels making them last for a much longer time.
- To reduce the pollution level and to save the environment.
(i). Solar Energy
- Sun is the ultimate source of energy.
- Energy obtained from the Sun is called solar energy.
- Energy received by the Earth per second per unit area from the Sun is known as solar constant.
Solar constant = 1.4 kJ/s/m2 Solar energy devices: Devices using solar energy are:
- Solar cooker
- Solar cells
- Solar water heater
- Solar Cooker
Box Type Solar Cooker: It consists of a rectangular box which is made up of wood or plastic which is painted dull black.
- Inner walls of the box are painted black to increase heat absorption.
- Solar cookers are covered with glass plate and have mirror to focus the rays of the sun and achieve higher temperature. Glass plate traps solar radiation by greenhouse effect.
- Temperature inside the box increases 100°C-140°C in 2-3 hours.
Advantages
- Save precious fuel like coal, LPG, kerosene.
- Does not produce smoke.
- Nutrients of food do not get destroyed while cooking.
- Upto four food items can be cooked at the same time.
- Renewable
- Can be used in rural areas.
Disadvantages
- Solar cookers cannot be used at night.
- If the day sky is covered with clouds, even then solar cooker cannot be used.
- Direction of reflector of solar cooker changes from time to time to keep it facing the sun.
- Solar radiations are not uniform over the Earth’s surface.
- Cannot be used for frying or baking purpose.
(ii) Solar Cell
- Solar cells convert solar energy into electricity.
- A solar cell develops a voltage of 0.5-1 V and can produce about 0.7 W of electricity.
- A large number of solar cells are combined in an arrangement called solar cell panel.
Advantages
- Have no moving parts.
- Require little maintenance.
- Can work without any focussing device.
- Can be set up in remote and inacessible areas.
Disadvantages
- Manufacturing is expensive.
- Availability of special grade silicon for making solar cells is limited.
- Silver wire for interconnection of cells is expensive.
Uses of Solar Cell
- Artificial satellites and space probes use solar cells as the main source of energy.
- Radio, TV relay stations in remote locations use solar cell panels.
- Traffic signals, calculators and many toys are fitted with solar cells.
2. Energy from the Sea
| Tidal Energy | Wave Energy | Ocean Thermal Energy | |
| Working: (i) | The phenomenon of high and low tide give us tidal energy. | Kinetic energy of huge waves near sea shore is trapped to generate electricity. | The difference in the temperature of water at the surface and deeper section of ocean is used to obtain energy in Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion plants (OTEC). |
| (ii) | It is harnessed by constructing a dam across the narrow opening of the sea. | Wave energy is used for rotation of turbine and production of electricity. | The warm surface water is used to boil volatile liquid ammonia. The vapours of the liquid are used to run the turbine of generator to produce electricity. |
| Disadvantage: | The location where such dams can be built are limited. | Wave energy is viable only where waves are very strong. | Efficient commercial exploitation is very difficult. |
3. Geothermal Energy
- ‘Geo’ means ‘earth’ and ‘thermal’ means ‘heat’.
- Geothermal energy is the heat energy from hot rocks present inside the earth.
- When underground water comes in contact with ‘hot spot’, steam is generated. Steam trapped in rocks is routed through pipes to a turbine and used to generate electricity.
Advantages
- Economical to use geothermal energy.
- Does not cause any pollution.
Disadvantages
- Geothermal energy is not available everywhere.
- Deep drilling in the earth to obtain geothermal energy is very difficult and expensive.
4. Nuclear Energy
- The energy released during a nuclear reaction is called nuclear energy.
- It can be obtained by two types of nuclear reactions:
(i) Nuclear fission
(ii) Nuclear fusion
(i) Nuclear Fission:
- ‘Fission’ means split up.
- The process in which the heavy nucleus of a radioactive atom (such as uranium, plutonium
or thorium) split up into smaller nuclei when bombarded with low energy neutrons, is called nuclear fission. - A tremendous amount of energy is produced.
- U-235 is used as a fuel in nuclear reactors in the form of uranium rods.
Working: In a nuclear reactor self sustaining chain reaction releases energy at a controlled rate, which is used to produce steam and further generate electricity.
(ii) Nuclear Fusion: When two nuclei of light elements (like hydrogen) combine to form a heavy nucleus (like helium) and tremendous amount of energy is released it is called nuclear fusion.
![]()
- Very-very high temperature and pressure is needed for fusion.
- Hydrogen bomb is based on this phenomenon.
- Nuclear fusion is the source of energy in the sun and other stars.
Advantages
- Production of large amount of useful energy from a very small amount of nuclear fuel.
- Does not produce greenhouse gases like C02.
Disadvantages
- Environmental contamination due to improper nuclear waste storage and its disposal.
- Risk of accidental leakage of harmful radiations.
- High cost of installation.
- Limited availability of nuclear fuel.
Environmental Consequences
Exploiting any source of energy disturbs the environment in some way or the other. Thus, the source we would choose depends upon the following factors:
- Ease of extracting energy from the source.
- Cost of extracting energy from the source.
- Efficiency of technology available to extract energy.
- The environmental damage caused by using that source.