CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Notes Light Shadows and Reflection
Light Shadows and Reflection Class 6 Notes Understanding the Lesson
1. Light is a form of energy. It enables us to see.
2. Light may be defined as an external physical cause that affects our eyes to produce the sensation of vision.
3. Light itself is not visible but in the presence of light other objects become visible.
4. There are some objects which have light of their own, g., torch, sun, etc. They are called luminous objects.
5. Objects which do not have light of their own are called non-luminous objects, g., chair, table, blackboard, etc. Such objects are visible only when light falls on it.
6. On the basis of passing of light through the objects, they are classified into three groups:
- Transparent,
- Translucent, and
- Opaque.
7. Objects which allow the light to pass through them are called transparent We can see clearly through them, e.g., clean air, clean glass, clean water, cellophane paper, etc.
8. Objects which allow only a small amount of light to pass through them are called translucent We cannot see very clearly through them, e.g., wax paper, greased paper, butter paper, frosted glass, etc.
9. The objects which do not allow light to pass through them are called opaque We cannot see through them at all e.g., clay, wood, metal, stone, etc.
10. A shadow may be defined as the dark area caused by an opaque object when it prevents light from passing to the other side. It is only a dark region having no colour.
11. A shadow is formed only when light rays are blocked by an opaque object.
12. The shape of a shadow depends upon the shape of the object.
13. The size of the shadow depends upon the distance between that source of light and the opaque object. If the distance between the source of light and an opaque object is more, the size of the shadow decreases and vice-versa (Fig. 11.1).
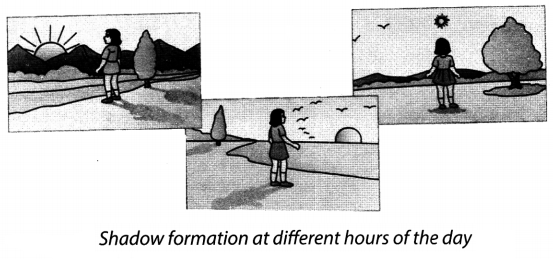
14. The shadow of an object is cast on the opposite side of the source of light.
15. The formation of shadow of one celestial body on the other is known as
16. When the moon comes in between the sun and the earth, the shadow of the moon falls on the earth. This phenomenon is known as solar eclipse.
17. When the earth comes in between the sun and the moon, the shadow of the earth falls on the moon. This is known as lunar eclipse.
18. A pinhole camera is a device which forms a photograph-like image of a bright object on a screen. It works on the principle that light travels in a straight line.
19. A pinhole camera can be made with simple materials and can be used to obtain the image of the sun and brightly lit objects.
20. Images formed by a pinhole camera are upside down. They are bright, real and inverted images.
21. There is an interesting pinhole camera in nature called a natural pinhole camera. When the sun rays falls on a tree, there are patches of sunlight of round shape seen on the ground. These circular shapes are, in fact, pinhole images of the sun. The gaps between the leaves, act as the pinholes.
22. Light always travels in a straight line. This is called rectilinear propagation of light.
23. The glass sheet which has a polished surface and the other surface remains shiny, smooth and reflective is called a mirror.
24. When a ray of light falls on a smooth polished surface of a mirror, it return back in the same medium. This phenomenon is called reflection of light. The ray of light that falls on a plane mirror is called incident ray and that returns back after reflection is called reflected ray. (Fig. 11.2).
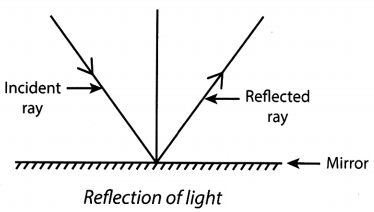
25. The image formed by a plane mirror is exactly of same size and colour as that of the object. It is erect and laterally inverted.
Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Notes Important Terms
Luminous objects: Objects that give out or emit light of their own are called luminous objects, e. g., sun, torch, bulb, etc.
Non-luminous objects: Objects that do not have light of their own are called non-luminous objects. They are visible only when light falls on them, e.g., chair, book, blackboard, etc.
Transparent objects: The objects which allow the light to pass through them are called transparent objects, e.g., water, air, glass, etc.
Translucent objects: The objects through which light can pass partially and through which we cannot see anything clearly are called translucent objects, g., greased paper, butter paper, thin paper, oily paper, frosted glass, etc.
Opaque objects: The substances which do not allow the light to completely pass through them are called opaque objects; g., cement sheet, wall, book, etc.
Shadow: The dark patches formed on the other side of opaque objects, opposite to the light source, are called shadow of the objects.
Pinhole camera: It is a device which forms a photograph-like image of a bright object on a screen is called pinhole camera. It is based on the principle that light always travels in a straight line.
Rectilinear propagation of light: Light always travels in a straight line. This property of light is known as rectilinear propagation of light.
Mirror: A glass sheet having a polished surface at one side and a shiny, smooth and reflective surface on the other side is called mirror.
Reflection: The phenomenon due to which light bounces off or returns back from a highly polished surface is called reflection of light.
Reflected ray: The ray of light that bounces off or returns back after suffering reflection from a mirror is called reflected ray.
Incident ray: The ray of light that falls on a plane mirror is called incident ray.
Eclipse: The formation of shadow of one celestial body on another in space is called eclipse.