CBSE Class 7 Maths Chapter 14 Notes Symmetry
Symmetry Class 7 Notes Conceptual Facts
Symmetry; If a paper is folded in half and the two halves of the paper exactly cover each other, then the shape of the paper is symmetric.
For example:
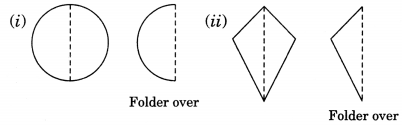
Axis of symmetry: When a figure is folded in half then the line of fold is called axis of symmetry.
For example:
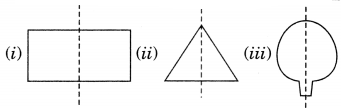
Symmetry of regular polygons:
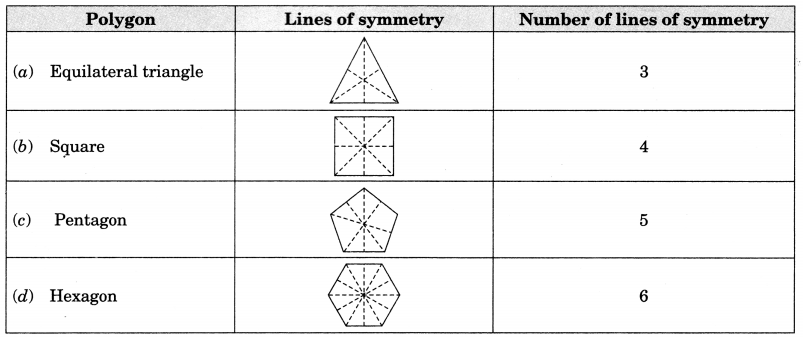
Note: Each regular polygon has a many lines of symmetry as it has sides.
Mirror reflection symmetry: The symmetry in which one half of the shape is the image of the other.
For example:
![]()
Rotational symmetry: When an object rotate clockwise or anticlockwise about a fixed point and when it looks after some rotation by a partial turn then it is called rotational symmetry. This fixed point is known as centre of rotation.
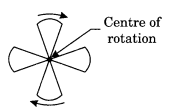
Axis of rotation: The line of symmetry about of which an object rotates is called the axis of rotation.
![]()
Angle of rotation: The angle through which an object rotates is called angle of rotations.
- A half-turn means rotation by 180°.
- A quarter-turn means rotations by 90°.
- A complete-turn means rotation by 360°.
Order of rotational symmetry: If x° be the smallest angle through which a figure can rotate and still looks the same, then the order of rotational symmetry \(=\left(\frac{360}{x}\right)\)
For example:
(i) Order of square \( =\frac{360}{90}=4\)
(ii) Order of equilateral triangle \( =\frac{360}{90}=6\)