CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Notes Light
Light Class 7 Notes Understanding the Lesson
1. Light is a form of energy which enables us to see objects from which it comes or from which it is reflected.
2. The objects which emit light of their own are known as luminous objects, g., the sun, lamp, candle, etc.
3. The objects which do not emit light of their own are known as non-luminous objects, g., chair, table, window, etc.
4. Light always travels in a straight line and this property of light is called rectilinear propagation of light.
5. Light falls on the surface of an object and the object sends the light back. This process of sending back the rays of light which fall on the surface of an object is called reflection of light.
6. The ray of light which falls on an object is called incident ray and the ray of light which is sent back by an object is called reflected ray.
7. A highly polished surface which is smooth enough to reflect a good fraction of light incident on it is called mirror.
8. An optical appearance produced by light or other radiations from an object reflected in the mirror or refracted through a lens is called
9. The image which can be formed or obtained on the screen is called a real image.
10. The image which cannot be obtained on the screen is called a virtual image.
11. The image formed by a plane mirror is erect, virtual and of the same size as the object.
12. Those mirrors whose reflecting surfaces are spherical or curved are called spherical mirrors.
13. There are two types of spherical mirrors:
- Concave mirror
- Convex mirror
14. When the reflecting surface of the spherical mirror is curved inwards, then it is called concave mirror.
15. A concave mirror can form a real and inverted image. When the object is placed very close to the mirror, the image formed is virtual, erect and magnified.
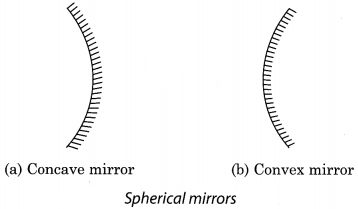
16. When the reflecting surface of the spherical mirror is curved outwards, then it is called convex mirror.
17. A convex mirror form erect, virtual, smaller size image of the object.
18. Lens is a piece of glass or transparent material with curved sides.
19. A lens that is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges is called a convex lens. It is also known as magnifying glass.
20. A convex lens can form real and inverted image. When the object is placed very close to the lens, the image formed is virtual, erect and magnified.
21. A lens that is thinner in the middle and thicker at the edges is called a concave lens.
22. A concave lens always forms erect, virtual and smaller image than the object.
23. White light is composed of seven colours. These are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet (acronym: VIBGYOR).
Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Notes Important Terms
Concave lens: It is also known as diverging lens. It is thinner at the centre than at the edges. It diverges a beam of light on refraction through it. Concave lenses have a virtual focus.
Concave mirror: The type of mirror in which reflecting surface of the spherical mirror is curved inwards, is called concave mirror.
Convex lens: Convex lenses are thicker at the centre and thinner at the edges. It converges a parallel beam of light on refraction through it. It has real focus.
Convex mirror: The type of mirror whose reflecting surface of the spherical mirror is curved outwards, is called convex mirror.
Erect image: When the image formed have same direction as that of object, then the formed image is called erect image.
Magnified image: When the size of image is larger than the object, then it is called magnified image.
Magnifying glass: A magnifying glass is a convex lens that is used to produce a magnified image of an object.
Prism: Prism is a transparent glass pyramid, bounded by four triangular surface that separates white light into a spectrum of colours.
Rainbow: A band of seven colours formed in the sky in the direction opposite to the sun due to rain or presence of water droplets in the atmosphere.
Real image: The image which can be formed or obtained on the screen is known as real image.
Rearview mirror: Rearview mirror is a mirror in automobiles and other vehicles, designed to see a virtual, upright and diminished image of the traffic behind them. For rearview mirror, convex mirror is used.
Side mirror: The rearview mirror is used as side mirror in motor vehicles.
Spherical mirror: ’he mirrors which have curved surfaces are known as spherical mirrors.
Virtual image: The image that cannot be obtained on the screen is known as virtual image.