CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Notes Understanding Quadrilaterals
Understanding Quadrilaterals Class 8 Notes Conceptual Facts
Polygon: A simple closed curve made up of only line segments is called a polygon.
Examples of Polygons:
(i) Triangle
(ii) Quadrilateral
(iii) Pentagon
(iv) Hexagon
Convex and concave polygons
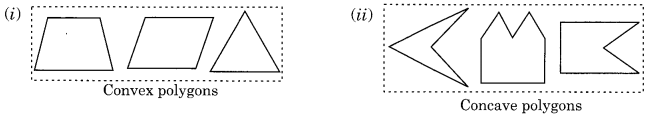
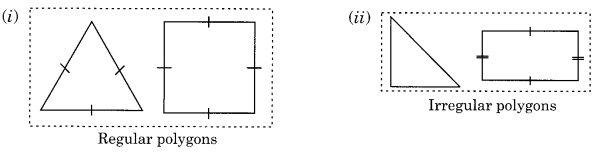
Regular and irregular polygons
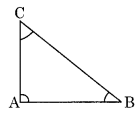
Angle sum property: The sum of three angles of a triangle is 180° In AABC, ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
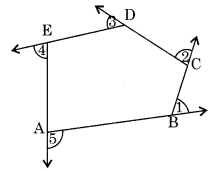
Sum of all the exterior angles of a polygon is 360°. In the given polygon ABODE, exterior angles ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 + ∠4 + ∠5 = 360°.
Kind of Quadrilaterals
(i) Parallelogram
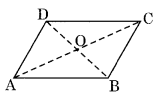
Properties
(a) Opposite angles are equal
(b) Opposite sides are equal
(c) Diagonals bisect each other
(ii) Rhombus:
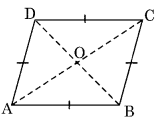
(a) All sides are equal
(b) Opposite angles are equal
(c) Diagonals bisect each other at 90°
(iii) Rectangle
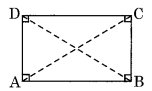
(a) It is a parallelogram having each angle of 90°
(b) Opposite sides are equal
(c) Diagonals are equal
(iv) Square:
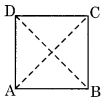
(a) All sides are equal
(b) Each angle is of 90°
(c) Diagonals are equal and bisect each other at 90°
(v) Kite:
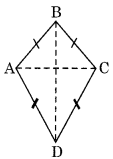
(a) Diagonals are perpendicular to each other.
(b) One of the diagonals bisects the other
(c) m∠A = m∠C but m∠B ≠ m∠D
(vi) Trapezium:
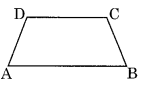
A pair of opposite sides is parallel to each other.