CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 Notes Statistics
Statistics Class 10 Notes Understanding the Lesson
The measures of central tendency are:
- Arithmetic mean or mean
- Median
- Mode
Mean of Raw Data
Mean of n observations x1; x2, x3, ..xn is given by
\(\bar{x}=\frac{x_{1}+x_{2}+x_{3}+\ldots+x_{n}}{n}=\frac{\Sigma x_{i}}{n}\)
where ∑ (sigma) means “summation of’.
1. Mean of Grouped Data
(i) Direct method:
\(\bar{x} \doteq \frac{\Sigma f_{i} x_{i}}{\Sigma f_{i}}\)
For each class interval, Class mark = \(\frac{\text { Lower limit }+\text { Upper limit }}{2}\)
(ii) Short-cut method or assumed mean method:
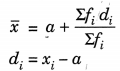
Where a = assumed mean
(iii) Step-deviation method:
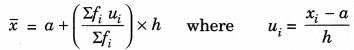
h=Class-Size
2. Mode of Groped Data
Class with the maximum frequency is called the modal class.
\(\text { Mode }=l+\left[\frac{f_{1}-f_{0}}{2 f_{1}-f_{0}-f_{2}}\right] \times h\)
Where l = lower limit of the modal class
h = size of the class-interval
f1 = frequency of the modal class
f0 – frequency of the class preceeding the modal class
f2 = frequency of the class succeeding the modal class
3. Median of Ungrouped Data
To find the median of ungrouped data, first arrange the data values of the observations in the ascending or descending order. Then,
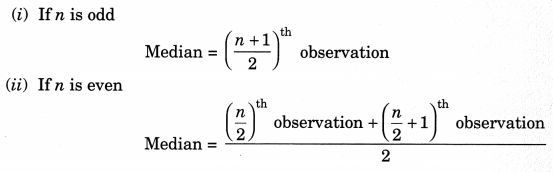
4. Median of Grouped Data
\(\text { Median }=l+\left[\frac{\frac{n}{2}-c \cdot f \cdot}{f}\right] \times h\)
l – lower limit of median class.
n = number of observation
c.f. = cumulative frequency of the class preceeding the median class
f = frequency of the median class
h = class size
Median class: Class whose cumulative frequency is greater than (and nearest to) \(\frac{n}{2}\)