CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Notes Fractions
Fractions Class 6 Notes Conceptual Facts
1. A fraction is a part of a whole number having numerator and denominator.
For example: \(\frac{5}{7}\) where 5 is numerator and 7 is the denominator.
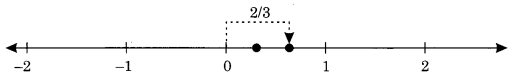
2. Representation of a fraction on a number line.
For example: \(\frac{2}{3}\)
3. Proper fractions: Numerator is less than the denominator.
For example: \(\frac{2}{3}, \frac{5}{8} \text { and } \frac{1}{5}\)
4. Improper fractions: Numerator is bigger than the denominator.
For example: \(\frac{5}{2}, \frac{7}{5}, \frac{10}{3} \text { and } \frac{6}{5}\)
5. Mixed fractions: It is represented by Quotient \(\frac{\text { Remainder }}{\text { Divisor }}\)
For example: \(5 \frac{1}{7}, 3 \frac{2}{3} \text { and } 4 \frac{5}{7}\)
6. Equivalent fractions: Two or more fractions are said to be equivalent fractions, if they represent the same quantity.
For example: \(\frac{2}{5}, \frac{6}{15}, \frac{4}{10} \text { and } \frac{8}{20}\)
7. Simplest form of a fraction: A fraction is said to be simple if numerator and the denominator have no common factor except 1.
For example: Simplest form of \(\frac{15}{20} \text { is } \frac{3}{4}\)
8. Like fractions: Two or more fractions having same denominators are called like fractions.
For example: \(\frac{2}{5}, \frac{3}{5}, \frac{4}{5}, \frac{6}{5}\)
9. Unlike fractions: Two or more fractions having different denominators are called unlike fractions.
For example: \(\frac{8}{9}, \frac{5}{7}, \frac{6}{5}, \frac{7}{10}\)